Can visual AI improve the customer experience? Yes, and here’s how


Visual artificial intelligence (AI) is changing how businesses interact with customers.
From analyzing product defects to verifying identities with facial recognition, visual AI opens the door to faster, more personalized engagement and support.
But while the potential is huge, so is the hesitation.
Many customers aren’t resistant so much as uncertain. Some lack understanding of how visual AI actually works to provide richer context that helps them get the right support. Others worry it might replace the human touch, instead of assisting agents in making more informed customer service decisions.
In reality, most buyers value the option to connect with a person — but don’t know that visual AI can actually make that human interaction stronger, smarter, and more empathetic.
That leaves one big question: can visual AI enhance the customer experience without eroding trust? Let’s find out.
Visual AI — also known as vision AI — is a type of artificial intelligence that helps computers “see” and make sense of the world through visual content like images and videos.
Instead of just working with text or numbers, visual AI processes multimodal information from:
Here’s a quick breakdown of how visual AI functions:
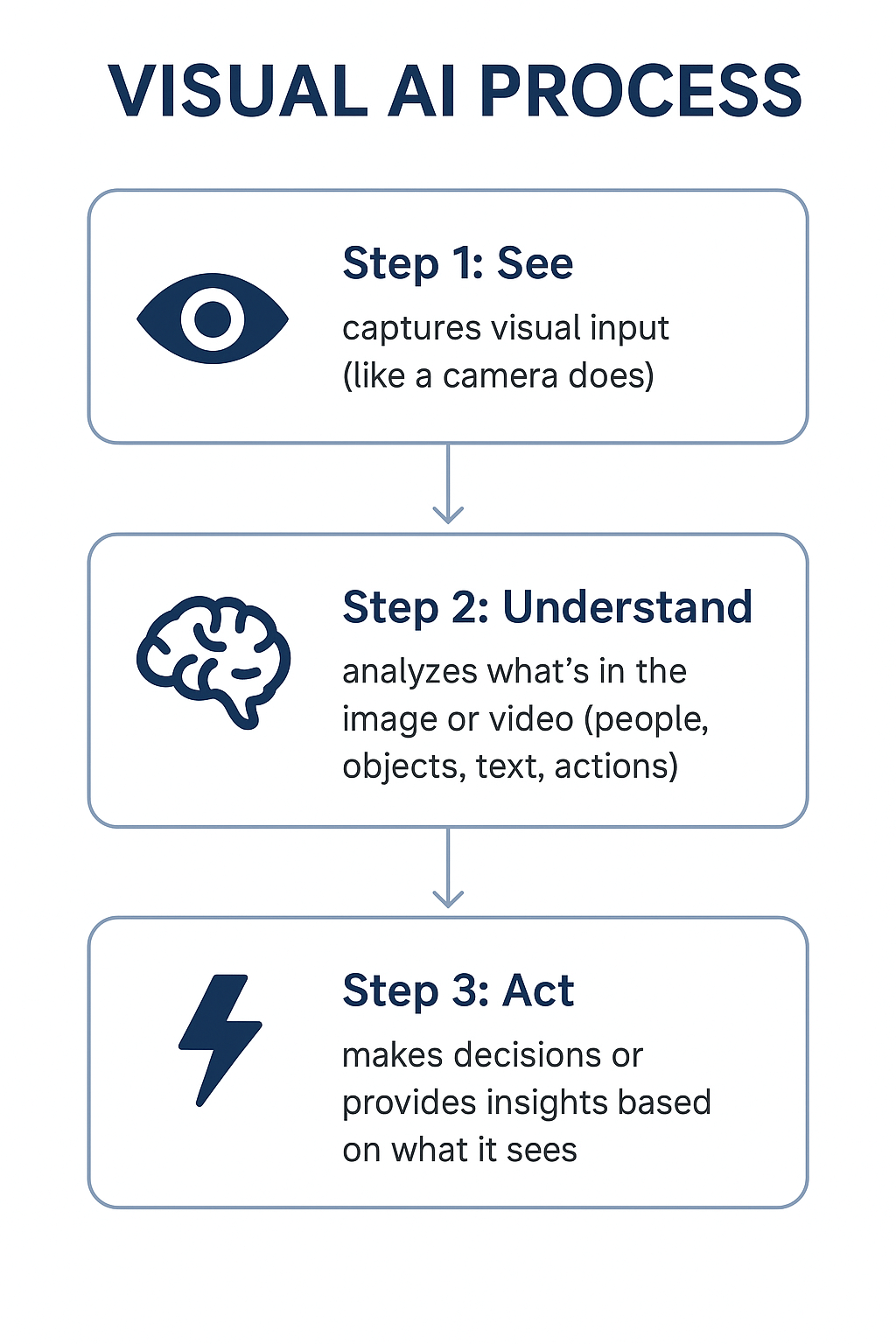
Visual AI uses computer vision and machine learning models to identify patterns, recognize objects, and even understand context.
It also includes deep learning and neural networks, a subset of machine learning that mimics how the human brain processes information to make decisions.
Real-world example: Imagine you’ve been in a minor car accident and need to file a claim with your insurer.
Instead of waiting for an assessor to visit or trying to explain the damage over the phone, you use your phone’s camera to upload photos and start a quick video call with the claims agent.
With visual AI, the insurer can:
The process feels seamless for the customer, while the insurer saves time, reduces errors, and handles claims more efficiently.
This is just one example of how visual AI can address buyer needs and enhance the customer experience (CX). Companies can also use it to visually diagnose technical issues, speed up product returns, improve fraud detection — the list goes on.
Computer vision and visual AI are often used interchangeably, but they’re not the same. Here are the key differences and roles they serve in creating intelligent customer experiences:
| Computer vision | Visual AI |
|---|---|
| Enables machines to see and interpret visual data (images, videos, live feeds) | Builds on computer vision by combining it with broader AI capabilities |
| Focuses on recognition tasks like object detection, motion tracking, and scene classification | Adds contextual understanding, predictions, and decision-making |
| Uses algorithms and models for image recognition, segmentation, and tracking | Integrates natural language processing (NLP), generative AI, and predictive modeling |
| Identifies what is present in an image or video | Infers intent, provides insights, and triggers actions |
Here’s a clear example of how computer vision feeds into visual AI:
To sum it up: Computer vision acts as the “eyes” of a machine, enabling it to see. Visual AI serves as the “brain,” interpreting what’s seen and deciding how to respond with insights, automation, and predictions.
In the next section, we’ll look at some visual AI use cases in more detail.
Visual AI covers a whole suite of capabilities that let machines see, interpret, and act on visual data.
From spotting defects on a factory line to analyzing customer behavior in a store, this AI technology unlocks insights that were once only possible for humans.
So what are the different types of visual AI and how do they work? Here’s a quick overview:
| Feature | Description & Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Behavioral analysis |
What it does: Understands how people and objects move and interact over time.
|
| Spatial analysis |
What it does: Tracks positioning, distances, and interactions in physical spaces.
|
| Optical character recognition (OCR) |
What it does: Converts text in images, videos, scans, or documents into searchable and editable datasets.
|
| Image recognition |
What it does: Identifies and classifies objects, people, or scenes in images and videos.
|
| Identity verification |
What it does: Scans facial features and documents to confirm identity in real time.
|
Let’s take an in-depth look at each type next.
Think of behavioral analysis as the step where computers don’t just see what’s happening.
Instead of simply recognizing that a person is in a room, visual AI can pick up on patterns. Are they walking in circles? Standing still too long? Moving unusually fast?
This kind of insight goes way beyond static images. It allows for spotting unusual activity, tracking trends, and even sending real-time alerts to keep environments safe and efficient.
Why it matters:
How to use behavioral analysis to improve CX — a real-world example:
Imagine a customer service center handling in-person store visits and live video or chat support.
Visual AI captures and analyzes behavioral signals — from facial expressions and micro-gestures to tone and engagement levels — so agents understand customer emotions more accurately.

Reading emotions correctly in real time enables customer service teams to escalate to the right person and assist the customer as effectively as possible.
For example, during a video support session, a customer may visibly show signs of impatience while troubleshooting a billing issue.
The AI system alerts the agent immediately and suggests actionable initiatives to exercise genuine empathy: slow down, show you understand their frustration, clarify instructions, or offer additional support options.
If the frustration continues, the AI can automatically escalate the session to a senior agent who can handle the customer’s issue better.
On the flip side, if the customer is calm and engaged, the AI may prompt the agent to suggest value-added services or new plans that enhance their experience with your service or product.
In these situations, customers feel truly understood, issues get resolved faster, and overall satisfaction increases.
Over time, visual AI measures these engagement patterns across sessions: frustration signals, moments of empathy, and emotional responses to different types of support.
These insights highlight common pain points, guide training programs, and refine support processes to continuously deliver better customer experiences across the board.
If behavioral analysis is about how things move, spatial analysis is about where they are.
Organizations can use it to see how rooms are used, how crowds are flowing, or whether safety standards are met. It’s about turning physical spaces into smart, responsive environments.
Why it matters:
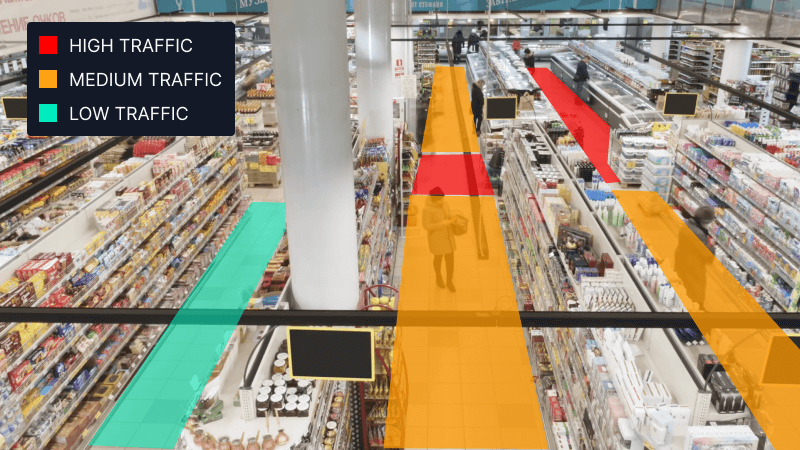
How to use spatial analysis to enhance CX — a real-world example:
Computer vision in retail helps stores monitor how shoppers move through aisles, how long they pause in certain areas, and where bottlenecks occur. If customers consistently linger near a display, managers can rearrange products to maximize sales.
It doesn’t stop there.
By predicting customer behavior and understanding traffic flows, retailers can prevent overcrowding, improve safety, and make the overall shopping experience smoother.
They can use visual AI insights to reduce or avoid unnecessary product returns. For example, by capturing detailed images from multiple angles, visual AI autonomously inspects returned products and compares them to predefined standards for damage or wear.
This process significantly reduces reliance on manual checks, eliminating much of the error and subjectivity.
When returns are necessary, visual AI automates quality inspections and defect detection, making return handling faster and more accurate.
OCR essentially gives machines the ability to read, whether it’s a crumpled receipt, a handwritten note, a video, or a scanned contract.
That means forms, IDs, and invoices can move seamlessly into digital systems without the slow, error-prone step of typing everything in manually.
Why it matters:
How to use OCR to enhance CX — a real-world example:
A telecoms company uses OCR to power virtual assistants for customers and support technicians. When a customer submits a handwritten service request or a scanned ID, OCR extracts the relevant information automatically.
For field technicians, OCR can scan and verify equipment labels or test results on-site, enabling faster quality checks and reducing errors during installations or maintenance.
By removing the slow, error-prone data entry steps, OCR helps the company resolve requests quickly, keeps technicians more productive, and ensures seamless handling of customer issues.
Image recognition is one of the most familiar applications of visual AI — and one of the most powerful.
From automatically tagging friends in social media posts to spotting a faulty part on an assembly line, image recognition takes over repetitive tasks that humans often spend a lot of time managing.
Why it matters:
How to use image recognition to enhance CX — a real-world example:
In retail service, agents can use image recognition to quickly identify a customer’s product and provide proper support.
For instance, when a customer reaches out about a washing machine issue, the AI scans the item, recognizes its exact model, and pulls up its service history, common problems, and troubleshooting guides.
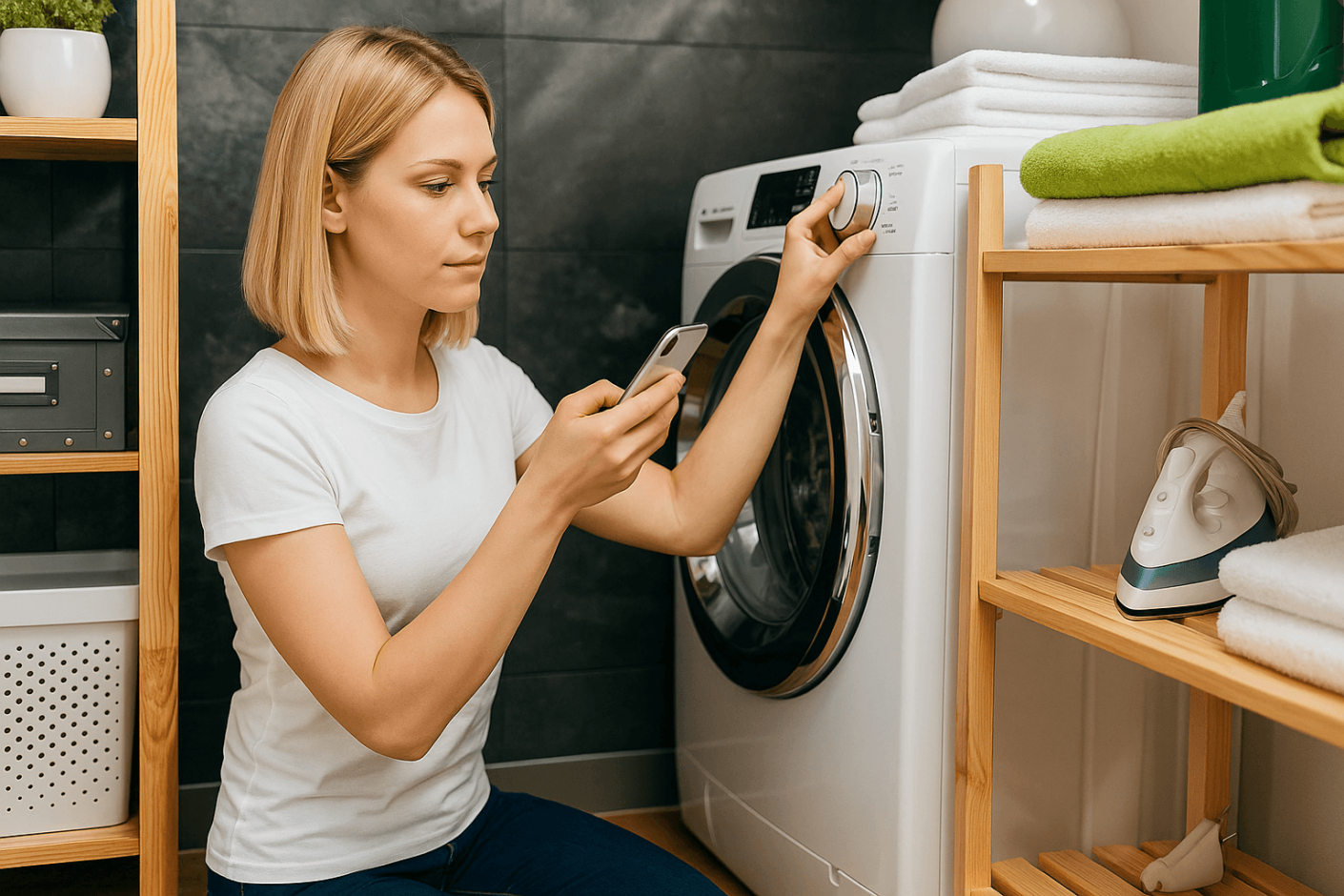

With all the information at hand, the support agent confidently recommends the best solution — whether it’s a quick fix, an on-site repair service, or a product replacement.
This efficient response reduces resolution time and minimizes customer frustration, ensuring prompt, accurate, and empathetic service.
ID verification software allows businesses to verify identities, streamline document checks, and classify commercial paperwork on the spot.
This visual AI application is transforming how businesses handle identity verification, or KYC (know your customer) processes.
Think of ID verification as a vigilant assistant working alongside your compliance and customer support teams. It handles time-consuming visual tasks so your human staff can focus on more complex verification issues or sensitive cases.
Why it matters:
How to use identity verification to enhance CX — a real-world example:
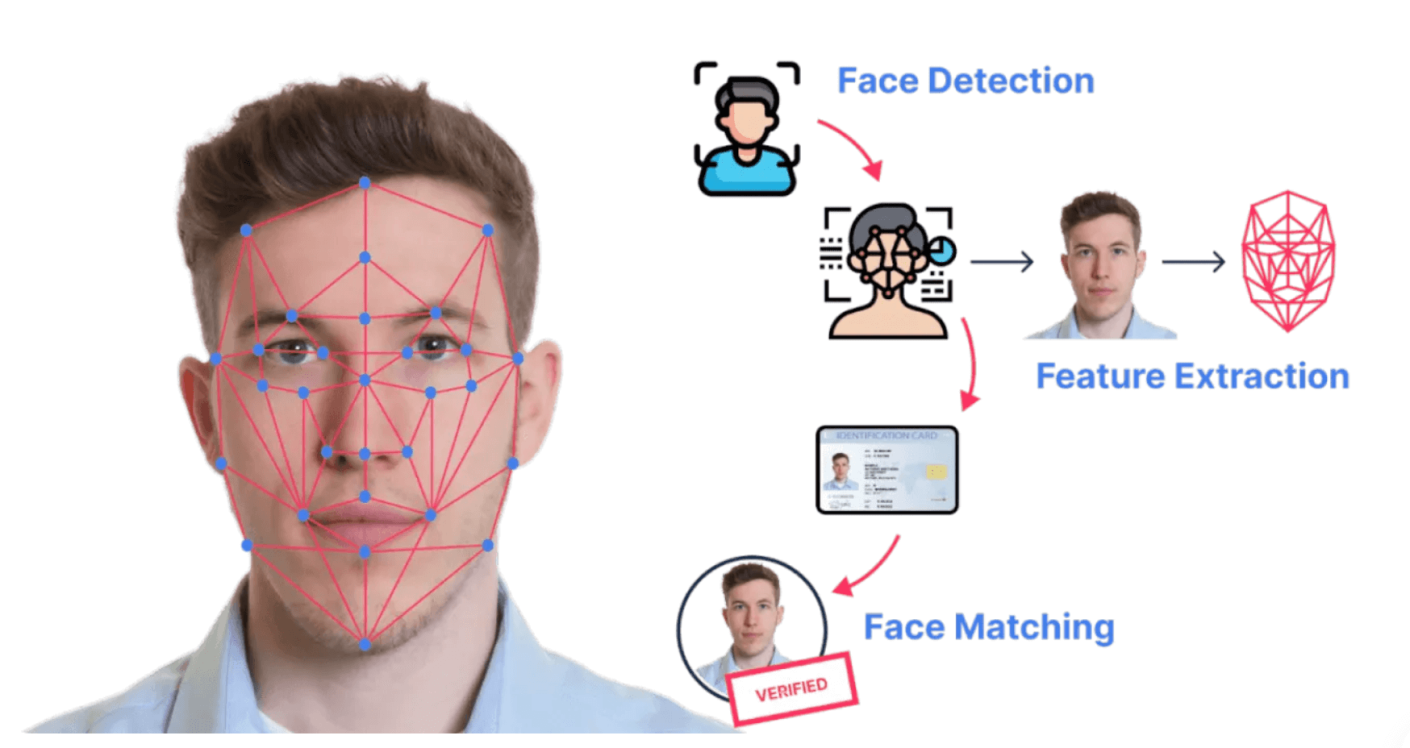
A banking app uses visual AI to simplify and secure the onboarding process. When a new customer signs up, the app prompts them to take a selfie and scan their government-issued ID.
Visual AI then analyzes the facial features in the selfie and compares them to the photo on the ID, detecting even subtle differences to prevent impersonation or fraud.
At the same time, the AI automatically reads and extracts the relevant information from the ID — like name, date of birth, and document number — eliminating the need for manual data entry.
Visual AI tools also classify and verify supporting documents, such as utility bills or proof of address, to ensure all paperwork meets compliance requirements. The AI flags any issues for human review, while immediately approving successfully verified identities.
This process not only reduces the risk of fraud, but also speeds up account access, providing customers with a smooth, secure, and near-instant experience.
To truly understand how visual AI delivers these powerful customer experience improvements, we must examine the computer vision technologies that make it all possible. We’ll explore these next.
Computer vision covers many functions and methods that form the technical foundation of visual AI systems, allowing them to process, interpret, and act on visual data.
Below are some of the most common computer vision tasks for analyzing and interpreting visual data in visual AI processes:
Here’s an example of image classification in a production environment:
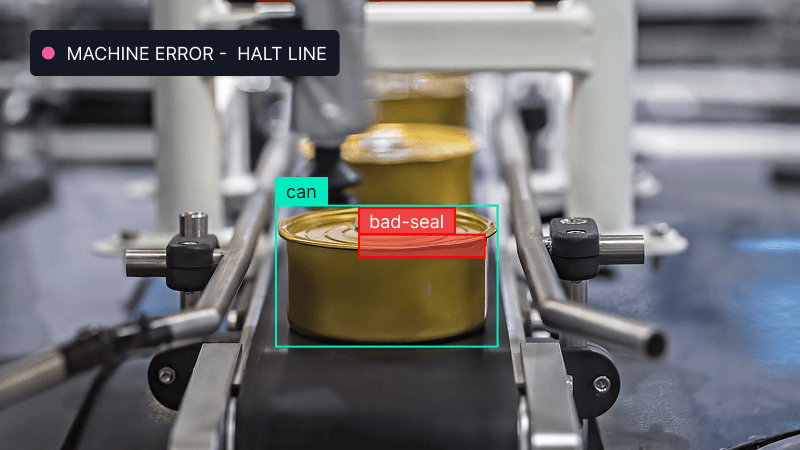
A manufacturing company can use computer vision within its visual AI system to detect defects — scratches, misaligned or missing components, and inconsistent designs — along the assembly line, flagging issues instantly.
Side note: The AI can track production metrics and monitor output quality, consistency, and defect patterns. Over time, this data helps manufacturers pinpoint recurring issues, optimize processes, minimize human error, and reduce waste.
There are also more specialized techniques that provide deeper and more advanced visual analysis. Here are some examples:
| Specialized computer vision task | What it does and how it helps |
|---|---|
| Optical flow |
|
| Visual odometry |
|
| Structure from motion (SfM) |
|
| Bag‑of‑visual‑words (BoVW) |
|
| Rigid motion segmentation |
|
| Neural radiance fields (NeRF) |
|
| Visual question answering (VQA) |
|
All these computer vision capabilities form the technical backbone that enables visual AI systems to deliver intelligent, context-aware customer experiences.
Building on this computer vision foundation, an AI agent represents the next step in intelligent customer service automation.
Vision AI agents (or visual AI agents) don’t just process text or commands — they see, analyze, and act on visual data independently.
The software combines multiple AI models to handle complex visual tasks automatically, turning raw images and video into actionable insights without constant human intervention.
At their core, vision AI agents rely on three main components.
Take a look at Atomicwork as an example. Its Universal AI agent uses visual AI to help employees with internal queries:
The agent interprets visual inputs, such as screenshots or screen shares, to diagnose issues and provide solutions without human input. Employees receive immediate assistance, reducing downtime and improving overall efficiency.
In short, vision AI agents don’t just observe — they reason, respond, and act. This visual AI autonomy opens new possibilities for smarter operations and faster decision-making across industries.
Customers expect support that’s quick, intuitive, and accurate. Studies show that 82% of service professionals agree that customer expectations are higher than they used to be.
Visual AI helps businesses meet these high expectations by turning visual information into actionable insights that guide faster, more precise responses.
Take Audi Reader. The AI app feature uses computer vision to let drivers scan and identify vehicle parts for instant automated guidance.
It’s tangible proof of visual AI delivering immediate, context-aware support.
Yet Gartner predicts that by 2027, 50% of organizations that expected to significantly reduce their customer service workforce by using AI to handle queries will abandon these plans.
64% of customers would also prefer that companies didn’t use AI for customer service and would like to speak to a person.
Why? Because people are still invaluable in the customer service process.
Visual AI-powered systems are powerful, but real value comes when they assist humans — not replace them.
Kathy Ross, Senior Director Analyst in the Gartner Customer Service and Support practice, says:
“The human touch remains irreplaceable in many interactions, and organizations must balance technology with human empathy and understanding. A hybrid approach, where AI and human agents work in tandem, is the most effective strategy for delivering exceptional customer experiences.”
Think of visual AI as a smart co-pilot for your customer support teams, helping them focus on the parts of the job that matter most and provide better customer service.
A customer support team might use visual AI to monitor emotional cues during video calls. More complex or sensitive situations — like property damage or banking inquiries — get escalated to human agents who can provide hands-on guidance and reassurance.
Consider Apizee as an example.
Businesses can use visual AI to handle parts of customer service that benefit from automation — like detecting defects in a product photo. When they cannot solve an issue automatically, a human touch is essential — which is where Apizee can help.
With Apizee, agents can launch a secure video call to see the problem first-hand, guide customers step by step, and provide the reassurance that only comes from speaking face to face.

Now, the question is, how do you know when to use visual AI?
In truth, it depends. The right use of visual AI relies on several factors:
Ultimately, you need a clear and well-defined customer service process. From here, you can understand which tasks benefit from speed, accuracy, or pattern detection.
Then, you can determine precisely where visual AI can provide support without replacing the human insight that keeps customers satisfied.
Visual AI is an exciting frontier for customer service, offering the ability to see, understand, and respond to customer needs in real time.
From analyzing video calls to reading facial cues, visual AI opens the door to faster, smarter, and more personalized end-to-end engagement and support.
Knowing how visual AI fits into your existing customer service process is key. Map your support workflows, identify tasks that benefit from quick visual analysis or pattern recognition, and determine where visual AI can assist without damaging the customer experience.
Discover how Apizee can help your team deliver faster, smarter, and more personalized CX and customer service through visual engagement.
Get a demoDiscover how the LEARN method helps customer service teams listen, empathize, and resolve issues more effectively—plus real examples and video support tips.
How the LEARN Method Improves Customer Service Communication
27 Jan 2026
Learn how the HEARD method helps customer service teams resolve complex issues with empathy, structure, and clarity—plus examples and video support tips.
How the HEARD Method Improves Customer Service (With Real Examples)
16 Jan 2026
Awaab's Law gives social housing tenants new rights from October 2025. Here’s what you need to know about the new UK legislation on damp and mould in social housing.
What is Awaab's Law? New UK Legislation for Social Landlords
16 Jan 2026
Interested in our solutions?